There are four basic types in accounting. These are Single-entry bookkeeping (Cost accounting), Single-entry tax accounting, Financial accounting, and Tax accounting. Each type serves a different purpose. The following information will help you get a general overview of them all. Find out more about each type of accounting. We will also be discussing single-entry bookkeeping in this article. This information will help you decide which one is right for you. Find out the differences and the benefits of each.
Cost accounting
There are many ways that cost accounting differs from traditional accounting. Cost accounting covers all costs that are involved in a company’s production, including variable and fixed. While fixed costs are recurring monthly and not affected by production levels; variable costs change in proportion to production costs. These costs include supplies and labor as well as equipment maintenance. Management uses the results of cost accounting to establish budgets and pricing for products/services.
This accounting type evaluates the cost of a business and how it affects efficiency, profit, or operations. This information is crucial for management as it allows them to decide how to cut costs and increase efficiency. Cost accounting does not need to be mandatory. It is not held to the same standards and guidelines as financial accounting. It still requires the same foundations and requires managerial judgement. For example, cost accountants are able to help management teams determine whether a given decision would affect the company's bottom line.
Single-entry bookkeeping
Single-entry bookkeeping allows for the recording of financial transactions in a simple and cost-effective way. It does not require any principles, making it an attractive choice for small and medium-sized businesses. This accounting system works well for small businesses, as it does not require the tracking of multiple people. It is also affordable as it doesn't require an expensive staff accountant. But single-entry bookkeeping does have its drawbacks.
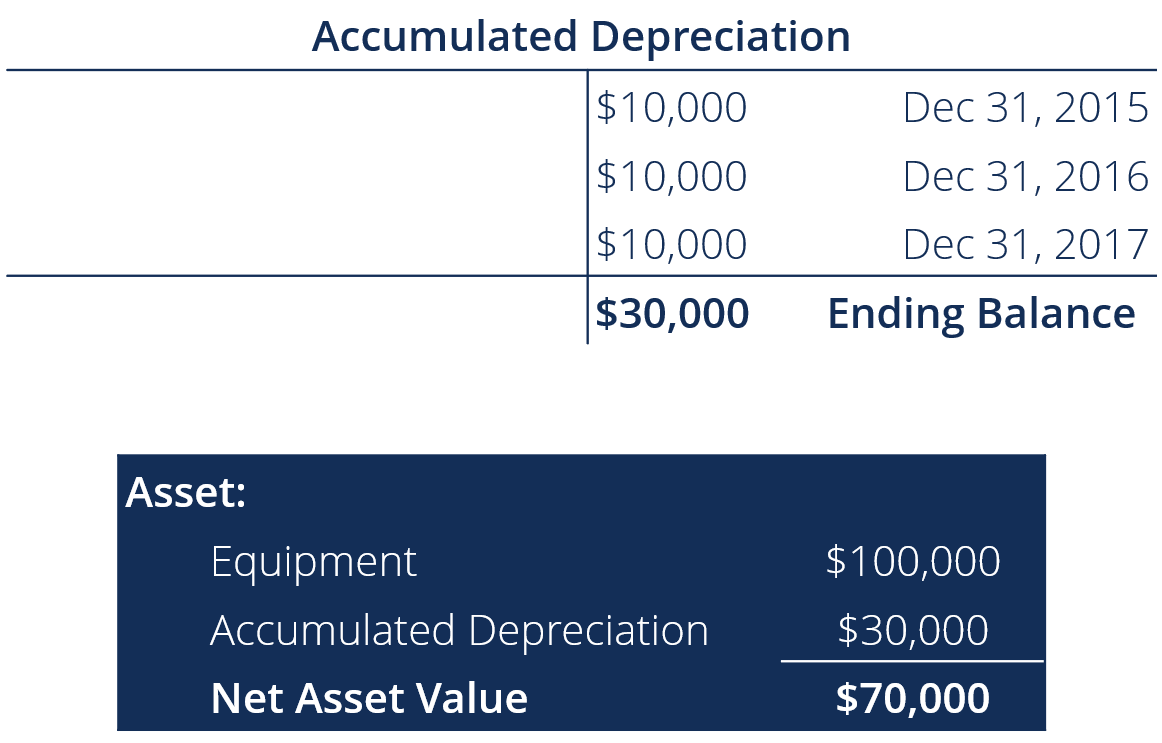
Single-entry accounting tracks only revenue and expenses in a business, just like the name. The balance sheet comprises assets, liabilities, owner equity. The accounts in single-entry bookkeeping are not consolidated and are only recorded once. Instead, the bookkeeper simply records the starting balance in a cashbook and notes the transactions beneath. At the end of each period, the bookkeeper calculates the total money.
Accounting for taxes
The main difference between tax accounting (and other types of accounting) is that the former is regulated and supervised by the Internal Revenue Service (HMRC). Tax accounting is derived from the Internal Revenue Code, and is completely separate from public financial statements. Tax accountants track all transactions that may affect a company's tax liabilities, calculate the amount of tax owed, and fill out the necessary forms for HMRC. Individuals may also benefit from the services of tax accountants, since they deal with wealthy individuals that need to minimize their tax liabilities.
Both types of accounting can be used by businesses. However, small businesses need to know that tax accounting focuses more on the preparation and filing of tax returns. Both individuals and businesses must be familiar with tax accounting regulations as they relate to filing and submitting tax return returns. Businesses, on the other hand, need to be more thorough with their expenditures and may benefit from the services of a tax accountant.
Financial accounting
There are generally twelve types of financial account. Each type is unique and practiced in a particular way. Accounting specialists tend to specialize in one particular area. Some accountants are critical to small-businesses. Accounting is an essential business activity. It involves the recording and categorizing of transactions. The information it provides investors with a broad picture of the company's economic stability. However, there is a difference between financial accounting and management accounting.
Financial accounting development is influenced by the social environment. There are many factors that can affect financial accounting. One factor is the country's level of development and inflation. This will often determine the kind of accounting practices used in the country. The type of accounting that is used can also be affected depending on the social environment. If a country has a higher level economic development than another, it may be that financial reporting is more important. And in many countries, political factors have a limited impact on financial reporting.
Management accounting

This is a type of financial management where the accountant uses quantitative as well as qualitative information to improve a company's financial performance and operations. Managerial accounting helps to define objectives, format plans, and make decisions that are crucial for the success of an organization. It is designed to provide useful information for managers. It also involves the use of standard costing and budget control to meet the needs of different departments and groups within the organization.
The profitability of a company is another major function of managerial accounting. Managerial accounting can be used to forecast the revenue and profits and to evaluate the underlying cost of the organization's activities. Managerial accounting also looks at trends and costs that could affect a company's ability for future decisions. These financial management techniques include capital budgeting as well as operational budgeting. They can also apply to other types or accounting.
FAQ
What is the best way to keep books?
To start keeping books, you will need some things. You will need a notebook, pencils and calculators, a printer, stapler, pen, stapler, envelopes and stamps, as well as a filing cabinet or drawer.
What is the difference in accounting and bookkeeping?
Accounting is the study and analysis of financial transactions. Bookkeeping is the documentation of such transactions.
The two are related but separate activities.
Accounting deals primarily in numbers while bookkeeping deals with people.
To report on an organization's financial situation, bookkeepers will keep financial information.
They adjust entries in accounts receivable and accounts payable to make sure that the books balance.
Accountants examine financial statements in order to determine whether they conform with generally accepted accounting practices (GAAP).
If not, they may recommend changes to GAAP.
For accountants to be able to analyze the data, bookkeepers must keep track of financial transactions.
What is the difference between a CPA and a Chartered Accountant?
Chartered accountants are professional accountants who have passed the required exams to earn the designation. Chartered accountants have more experience than CPAs.
Chartered accountants also have the ability to provide tax advice.
To complete a chartered accountant course, it takes about 6 years.
What does an accountant do and why is it important?
An accountant tracks all your money, both earned and spent. They also record how much tax you pay and what deductions are allowable.
An accountant will help you manage your finances, keeping track of both your incomes as well as your expenses.
They assist in the preparation of financial reports for both individuals and businesses.
Accounting professionals are required because they need to be able to understand all aspects of the numbers.
In addition, accountants help people file taxes and ensure they're paying as little tax as possible.
What's the purpose of accounting?
Accounting provides a view of financial performance by measuring and recording transactions, analyzing them, and reporting on them. Accounting allows organizations make informed decisions about how much money to invest, how likely they are to earn from their operations, and whether or not they need to raise additional capital.
Accounting professionals record transactions to provide financial information.
The data collected allows the organization to plan its future business strategy and budget.
It is essential that data be accurate and reliable.
How can I tell if my company has a need for an accountant?
Companies often hire accountants once they reach certain sizes. One example is a company that has annual sales of $10 million or more.
Many companies employ accountants regardless of size. These include small firms, sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations.
A company's size doesn't matter. The only thing that matters is whether the company uses accounting systems.
If it does, then the accountant is needed. A different scenario is not possible.
Statistics
- In fact, a TD Bank survey polled over 500 U.S. small business owners discovered that bookkeeping is their most hated, with the next most hated task falling a whopping 24% behind. (kpmgspark.com)
- Employment of accountants and auditors is projected to grow four percent through 2029, according to the BLS—a rate of growth that is about average for all occupations nationwide.1 (rasmussen.edu)
- a little over 40% of accountants have earned a bachelor's degree. (yourfreecareertest.com)
- a little over 40% of accountants have earned a bachelor's degree. (yourfreecareertest.com)
- Given that over 40% of people in this career field have earned a bachelor's degree, we're listing a bachelor's degree in accounting as step one so you can be competitive in the job market. (yourfreecareertest.com)
External Links
How To
How to Become a Accountant
Accounting is the science that records transactions and analyzes financial data. Accounting also includes the preparation of statements and reports for different purposes.
A Certified Public Accountant is someone who has passed and been licensed by the state board.
An Accredited Financial Advisor (AFA), is an individual that meets certain criteria established by American Association of Individual Investors. A minimum of five year's investment experience is required before an individual can be made an AFA. They must pass a series exam to verify their understanding of accounting principles.
A Chartered Professional Accountant, also known as a chartered accountant or chartered accountant, a professional accountant who holds a degree from a recognized university. The Institute of Chartered Accountants of England & Wales (ICAEW) has established specific educational standards for CPAs.
A Certified Management Accountant, also known as a CMA, is a certified professional who specializes on management accounting. CMAs have to pass exams administered by ICAEW and keep up-to-date with continuing education requirements throughout the course of their careers.
A Certified General Accountant (CGA) member of the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA). CGAs are required to take several tests; one of these tests is known as the Uniform Certification Examination (UCE).
International Society of Cost Estimators has awarded the certification of Certified Information Systems Auditor. Candidates for the CIA must have completed three levels of education: coursework, practical training, then a final exam.
An Accredited Corporate Compliance Officer (ACCO) is a designation granted by the ACCO Foundation and the International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO). ACOs must possess a Bachelor's Degree in Finance, Business Administration, Economics, or Public Policy. They must pass two written exams, and one oral exam.
The National Association of State Boards of Accountancy's Certified Fraud Examiner credential (CFE), is awarded by NASBA. Candidates must pass three exams with a minimum score 70 percent.
International Federation of Accountants is accredited a Certified Internal Audior (CIA). The four-part exam covers topics such as auditing (auditing), risk assessment, fraud prevention and ethics, and compliance.
An Associate in Forensic Accounting (AFE) is a designation given by the American Academy of Forensic Sciences (AAFS). AFEs must be graduates of an accredited college or university that has a bachelor's in accounting.
What is an auditor? Auditors are professionals who audit financial reporting and internal controls of an organization. Audits may be conducted on a random basis, or based in part on complaints made by regulators.